- Frozen foods have less nutrients than fresh food – as we have already cleared that this is a major myth regarding frozen foods. It was seen that fresh fruits and vegetables usually lose nutrients more rapidly than canned or frozen products. Fresh produce loses vitamins upon refrigerated storage over time, while their frozen counterparts retain these nutrients equally so or better. The concentrations measured in frozen produce generally resembled those observed in the corresponding fresh produce prior to refrigerated storage.

2. Freezing will kill all the bacteria – yes and no, as certain bacteria may die at a freezing temperature, but not all. Some bacteria can survive freezing temperatures. Freezing to 0 deg F (-17.8deg C) inactivates any microbes, bacteria, yeasts and moulds present in food, most of them enter a dormant state and stay alive in the frozen food or liquid.
Once thawed, however, these microbes can again become active, multiplying under the right conditions to levels that can lead to foodborne illness. It’s the heating of the food, which will destroy most of them. (Thawing is the process of taking a frozen product from frozen to a temperature (usually above 0deg C) where there is no residual ice, i.e. “defrosting”. Thawing is often considered as simply the reversal of the freezing process.)
3. Frozen foods are processed foods – yes & no. Yes, if the frozen food itself is processed food like frozen pizzas, processed meats, frozen fried foods. But you don’t freeze only processed foods, but extremely healthy fruits and vegetables too. For e.g. frozen peas, carrots, fresh meats, fruits, berries etc. Another way to check the quality of processed foods is by reading the ingredient list behind it. The list should be minimal in terms of preservatives and additives.

4. Frozen foods are high in sodium – just like processed food thought pattern, most people automatically conclude that all frozen foods would have high sodium. This is because salt/sodium is one of the oldest and cheapest preservatives and it also enhances flavour. But with rising health concerns, more and more companies are offering low-sodium options. Also, mostly the sodium content is found high in processed frozen foods, not healthy frozen foods. Try looking for frozen foods with sodium content not over 300-500mg.
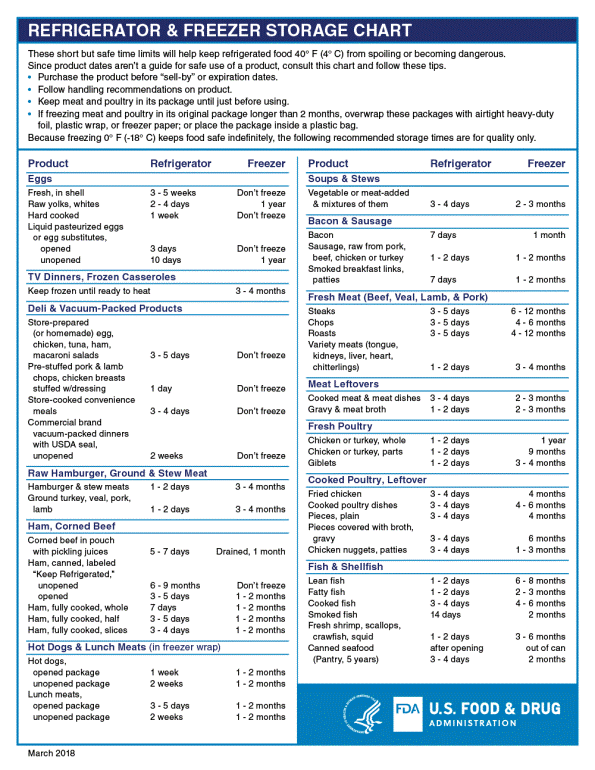
5. For how long can we store frozen foods? – a common doubt people ask. Though freezing can really extend the shelf-life of foods for quite long, but eventually all foods will gradually lose their freshness and flavours. Though most frozen foods in the market has the time limit listed on the label, about how long can that food be frozen. The freezing time differs from food to food and can last from 1 to up to 12 months.
Below is the chart by US FDA, indicating the freezing and refrigeration time for various foods: