Women generally have a higher percentage of body fat storage than men. And body fat percentage also increases with age. That’s why there are different ranges of fat percentages which are considered for men & women, depending on their age groups.
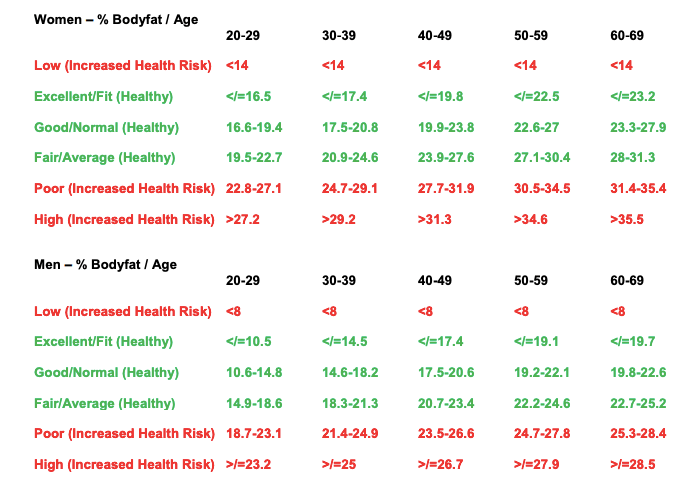
The average healthy adult body fat range regardless of age is 15 to 20% for men and 20 to 25% for women. A woman with more than 32% body fat and males with more than 25% body fat are considered to be at increased risk for disease.
The research also states that, trained athletes tend to be at the low end of this scale due to their increased lean weight (muscle mass) compared to untrained individuals. While low levels of body fat seem to be related to improved performance, body composition alone is not a great predictor of sports success. There is little evidence of any health benefit when men drop under 8% and women drop under 14% body fat.
The way excess fat percentage poses health & disease risk, same is the case with very low fat percentage. You need a certain amount of fat for the body to function normally and remain healthy.

Body fat percentage measurements calculate total body fat. This total body fat can be split into the following 2 categories:
- Storage Fat – This consists mainly of fat deposited just under the skin or subcutaneous fat. Storage fat for men and women is fairly similar. For the average man 12% of bodyweight is storage fat and for the average woman 15% of bodyweight is storage fat.
- Essential Body Fat – Essential fat is the amount of fat necessary for maintenance of life and reproductive functions. It acts like energy reserve, help conserve body heat, and protect the internal organs & joints from injury. For women the average amount of essential fat is 13% of bodyweight and for men it is 3% (in some studies it is suggested 4-6%).

Very low body fat percentages can lead to various health complications like Nutritional deficiencies & Electrolyte imbalance, which can cause:
- Heart complications – a study which tracked a drug-free male bodybuilder (age 26-27y) for the 6 months before and after a competition, found that his:
- Heart rate decreased from 53 to 27 beats/min during preparation and increased to 46 beats/min within 1 month after competition.
- Blood pressure dropped from 132/69 to 104/56 mmHg during preparation and returned to 116/64 mmHg at 6 months after competition.
- Percent body fat declined from 14.8% to 4.5% during preparation and returned to 14.6% during recovery.
2. Heart rate decreased from 53 to 27 beats/min during preparation and increased to 46 beats/min within 1 month after competition. Blood pressure dropped from 132/69 to 104/56 mmHg during preparation and returned to 116/64 mmHg at 6 months after competition. Percent body fat declined from 14.8% to 4.5% during preparation and returned to 14.6% during recovery.
3. Mood fluctuations – of course when the overall energy levels dip, the mood changes will happen. In the above study, total mood disturbance increased from 6 to 43 units during preparation and recovered to 4 units 6 months after competition.
4. Low Libido – the above study also found that the testosterone levels of the bodybuilder during competition declined from 9.22 to 2.27ng/mL during preparation and returned back to the baseline level, 9.91ng/mL, after competition.
5. Strength level plummets – the above study showed that, in the tested bodybuilder, the strength decreased during preparation and did not fully recover during 6 months of recovery.
6. Multiple nutritional deficiencies – as many vitamins and minerals need fat for proper absorption in the body. To maintain a low fat percentage, of course the fat intake would be too low, which will lead to deficiencies in vitamins like A, D, E & K, which have their own respective complications. Night blindness, swollen gums, slow wound healing, muscle pain, loose teeth etc. are just some of the issues.
7. Bone Loss – low levels of body fat percentage reduces the body’s absorption of important vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D.
8. Fertility issues – women need much more fat than men, for child bearing. And a women needs adequate amount of fat in the body to increase fertility rates, and in case the fat percentage goes low, then it becomes even difficult to sustain the pregnancy. Acc. to a study, a minimum ratio of fat to lean mass is normally necessary for menarche (app. 17% fat/body wt) and the maintenance of female reproductive ability (app. 22% fat/body wt).
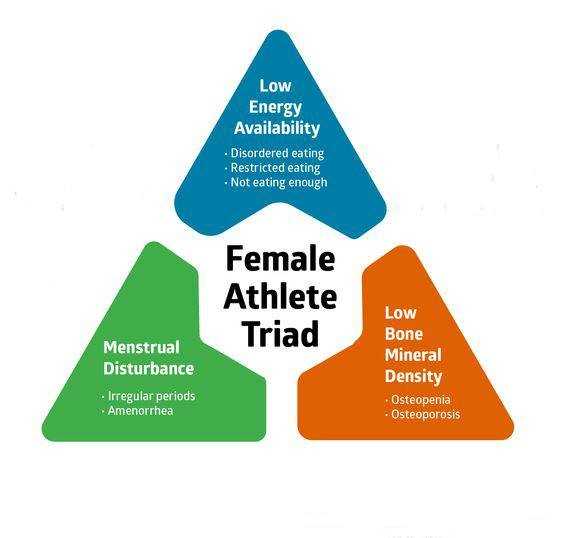
9. Female Athlete Triad (FAT) – female athletes who need to maintain very low fat percentage, like fitness models, bodybuilders etc. experience a disorder called FAT, leading to 1) low energy availability with or without disordered eating 2) menstrual irregularities or amenorrhea and 3) low bone mineral density.
10. Skin & Hair problems – fat forms an essential part of your skin structure and helps your skin maintain its moisture barrier. Very low fat intake of going very low on fat percentage, can lead to skin issues like dermatitis, which is shown as dry and scaly rashes on the skin.
Studies have shown that, deficiency of the polyunsaturated essential fatty acids linoleic acid (omega-6 fatty acid) and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3 fatty acid), can lead to loss of scalp hair and eyebrows as well as lightening of hair. The study also showed the benefits of various fat soluble vitamins like A, E, & D on hair loss.
11. Low immunity & Frequent illness – a study found that, trained runners who severely limit the amount of fat in their diets may be suppressing their immune system and increasing their susceptibility to infections and inflammation.
Researchers found that, natural killer cells, a type of leukocyte and one of the body’s defence mechanisms marshalled to fight infection, were more than doubled in runners after the high-fat diet, compared to the low-fat regimen. Levels of PGE2, inflammation-causing prostaglandins, increased after the endurance test and were higher when the runners were on the low-fat diet.



